An Example of a Type I Subsequent Event Is:
As you are performing due diligence in your audits you take subsequent events into account. The nature of the event and.

Weekly Activity Report Template New How To Write A Weekly Report Template Sazak Mouldings Co Report Template Operations Management Book Report Templates
An example of a Type I subsequent event is.

. Purchases and sales of Property plant and equipment and investments. A tornado that destroys an entitys factory after the balance sheet date. Which of the following is a Type II subsequent event.
An example of a Type I subsequent event is. Type II subsequent events provide evidence about conditions that did not exist on or before the balance sheet date. There are generally two types of subsequent events.
An event after the balance sheet date that confirms the auditors belief documented prior to the end of the entitys fiscal year that. Per the Financial Accounting Standards Board FASB Accounting Standards Codification ASC 855-10-20 Subsequent Events are defined as events or transactions that occur after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. Events occurred after a before b a balance sheet date.
1The first is a recognized event whereas the second is a non-recognized. An example of a Type I subsequent event is. After before between close to near on 2.
In private companies its before the date. It might be misleading to issue the statements as they are at period end. Pages 68 Ratings 100 20 20 out of 20 people found this document helpful.
Nonrecognized subsequent events see FSP 286 are considered for disclosure based on their nature to keep the financial statements from being misleading. Bankruptcy of a customer subsequent to year-end which would be considered when evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for uncollectible accounts. An example of a type i subsequent event is a a.
As usual the date of issue annual report is around two to three weeks after the reporting date. A subsequent event is a real event occurring after the date of the balance sheet but before the issuance of the financial statements of a public company. An event that provides additional information about pre-existing conditions that existed on the balance sheet date.
There are two types of subsequent events. Sale of a bond or capital stock issue. These events are disclosed but are not recognized in the financial statements.
The two types of subsequent events are noted below. A subsequent event is an event that occurs after a reporting period but before the financial statements for that period have been issued or are available to be issued. Purchase of a business.
There are two types of subsequent events. Depending on the situation such events may or may not require disclosure in an organizations financial statements. School Louisiana State University.
An event after the balance sheet date that confirms the auditors belief documented prior to the end of the entitys fiscal year that. If a reporting entity determines that disclosure is necessary ASC 855-10-50-2 indicates that it should include. The problem arises for companies because subsequent event accounting could dramatically alter an investors opinion.
Provide evidence about conditions existed at. Examples of non-adjusting subsequent events include. Date of financial statements become available to be issued.
Subsequent Events 2269 AU Section 560 Subsequent Events Source. An example of a subsequent event that is an adjusting event is the settlement of a lawsuit that happened before the balance sheet date. The consequences of natural disaster such as flood or earthquake.
Course Title ACCT 3222. The 2 types of subsequent events. Issues of shares and loan stocks.
Sale of a bond or capital stock issue. The purchase or sale of a business segment the sale of a large amount of stock or the issuance of bond and events that create catastrophic losses for. A tornado that destroys an entitys factory after the balance sheet date.
06 Examples of events of the second type that require disclosure to the financial statements but should not result in adjustment are. 06 Examples of events of the second type that require disclosure to the financial statements but should not result in adjustment are. A subsequent event that provides new information about a condition that did not exist on the balance sheet date.
An example of a Type I subsequent. Two types of subsequent events. There are two types of subsequent events relevant to financial statement audits.
Type 1 subsequent events involve events that existed ___ the balance sheet date. And it also depends on the auditor who signed on. Opening new trading activities or extending existing trading.
The two types of subsequent events are. Financial statements are issued. 2861 Disclosure requirements for nonrecognized subsequent events.
It depends on the size and complexity of the company business. There are three Type II events that you should investigate to determine whether you need to disclose in the financial statements. While all subsequent events should be reported not all of them are formally recognized and baked into the financial statements.
It also provides evidence about the conditions that affect the estimates. Settlement of litigation when the event giving rise to the claim took place subsequent to the balance-sheet date. The two events are Type I and Type II events.
Subsequent Event is the event that occurs after the reporting date but before the date of issue financial statement. An amount received related to an insurance claim that was in the course of negotiation at year-end. Widely distributed for general use.
Available to be issued. This problem has been solved. B date of financial statements are issued.
Type 1 subsequent events require ___ of the financial statements. Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. An example of a type I event is litigation where the event leading to the claim occurred during one year but is settled during the following year.
Subsequent Events Meaning. All necessary approvals were obtained to be issued. Type I events provide evidence about conditions that existed at the date of the balance sheet.
A tornado that destroys an entitys factory after the balance sheet date. For example a Type I event may be an account. An example of a Type I subsequent event is A A tornado that destroys a clients.
An event after the balance sheet date that confirms the auditors belief documented prior to the end of the entitys fiscal year that a large portion of the entitys inventory is obsolete. Change of principal activities. An estimate of the impact on the financial statements or an assertion that an estimate cannot be made.
An example is a natural disaster that destroys a facility after the balance sheet date.

24 Free Memo Templates Printable Word Excel Pdf Formats Memo Template Memo Templates
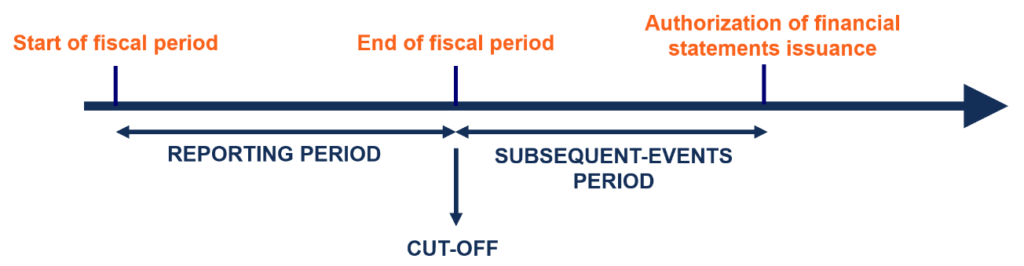
Subsequent Events Accounting For Events After The Fiscal Year

This Is An Example Of A Data Reduction Diagram Notice How The Exclusions Are Put Off To The Right And The Records That Are Kept Go Cohort Study Study Patient

Ux Research Design For Grocery Shopping Service Grocery Information Architecture Competitive Analysis
Comments
Post a Comment